UAV-based monitoring and quantification of greenhouse gas emissions
1. Enhanced Uncrewed Aerial Vehicle Techniques for Monitoring Greenhouse Gas Plumes at Point Sources
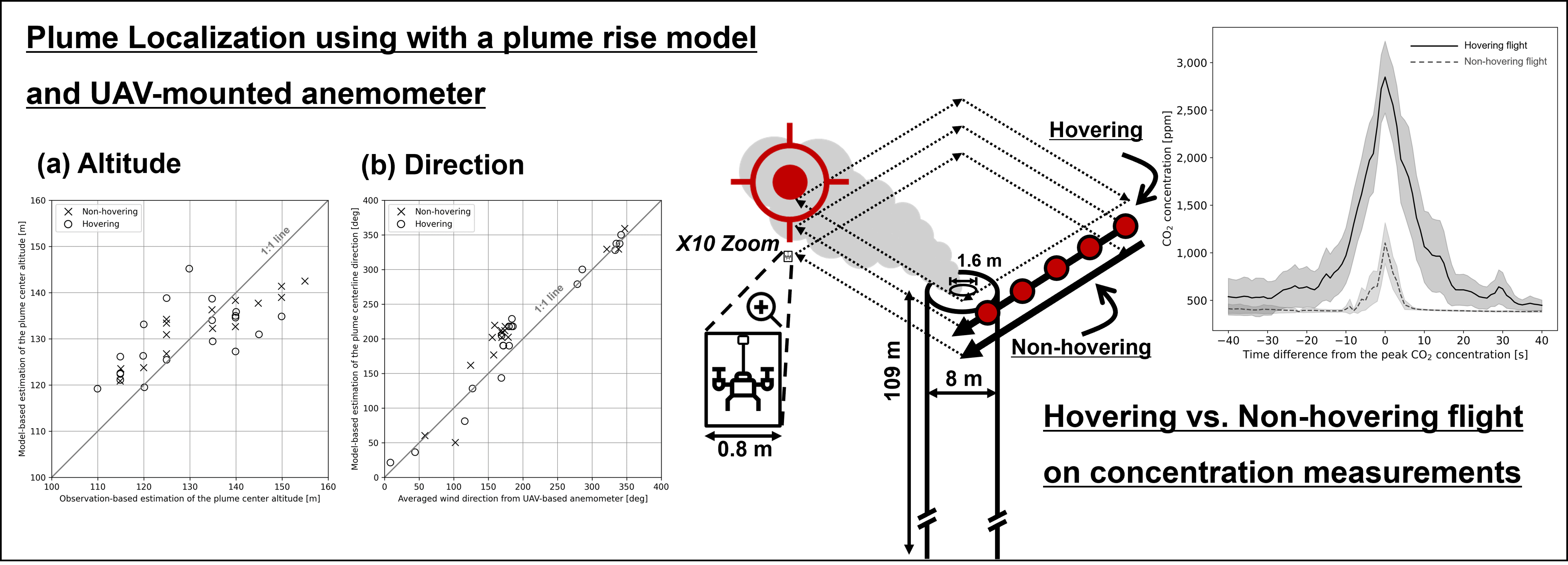
This study investigates the application of uncrewed aerial vehicles (UAVs) to improve monitoring techniques for greenhouse gas emissions, with a specific focus on measuring CO2 concentrations from point sources, such as incinerators. The UAV system was equipped with a Non-Dispersive Infrared Absorption (NDIR) CO2 sensor to provide real-time measurements of CO2 levels. An autopilot system, combined with plume localization based on Brigg’s plume rise model and an anemometer mounted on the UAV, enabled efficient plume detection. The findings demonstrate that this UAV-based approach is capable of accurately capturing plume dynamics, offering potential advancements in emission monitoring and measurement techniques.
Check out Journal Paper for more information.
2. Uncrewed Aerial Vehicle-Based CO2 Emission Quantification from Municipal Solid Waste Incinerators
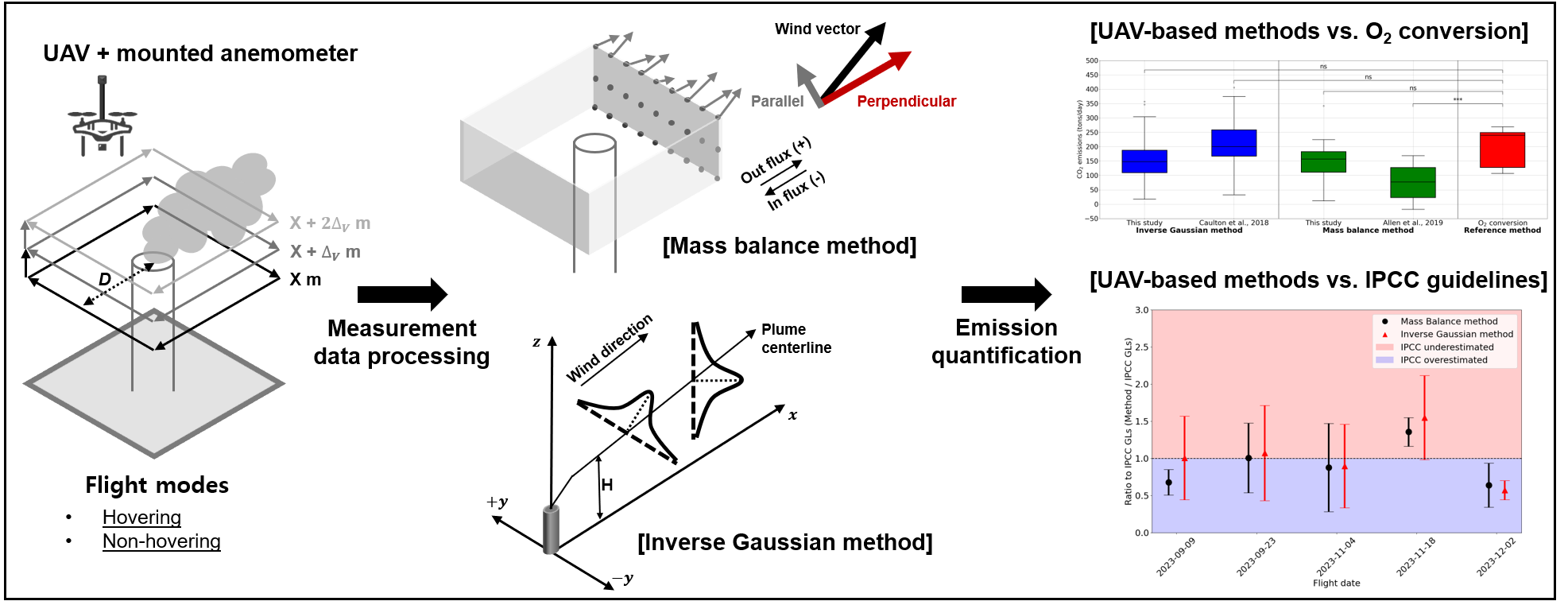
This research quantifies CO2 emissions from a municipal solid waste incinerator using UAVs and compares two key methods: the mass balance method and the inverse Gaussian method. Real-time wind measurements by UAV-mounted anemometer were incorporated to improve the accuracy of emissions quantification. The study found that the mass balance method, particularly when utilizing real-time wind data, provided the most accurate results, reducing the error rate significantly compared to traditional methods. The study also highlights the critical role of high-resolution wind data in improving emission quantification accuracy and offers insights into refining UAV-based monitoring technologies for industrial greenhouse gas emissions.
